Unique, environmentally friendly waste recycling technology |
 
|
It is known that the life function of man is associated with the production of decomposition products, food and industrial waste (1.5 liters per day). Some of this waste must be treated in the right way, otherwise it can cause serious environmental damage. In addition, the period of degradation of many materials is more than a hundred years. The heavy pollution of the planet and the unsolved garbage problem have led to global changes - the destruction of the environment for living organisms. Garbage disposal, especially in large cities, has become a big problem of our time. None of the developed or developing countries can boast of having a well-established waste recycling system. Nowadays, only up to 70% of waste gets a second existence through recycling, and what do you have to do with the remaining 30%? Incineration or landfilling is not a rational option, which further exacerbates the already tense situation.
The global trend to recycle as much as possible causes manufacturers of machinery and equipment to build specialized mini-plants that have many advantages over landfill:
- up to 95% of waste is recycled;
- they take up little space;
- the constructions are mobile - this makes it possible to place the plant near landfills and large enterprises;
- quick payback - you can get a net profit in the first two years of operation of a mini-plant;
- Environmental friendliness-Recycling does not pollute the environment and does not cause toxic emissions to the atmosphere or nearby water bodies;
- Minimum number of employees involved in the action.
Approximate composition of municipal solid waste in the city. The morphological composition varies from country to country and from region to region!

The main stages of the investigation are:
Table of waste hazard classes:
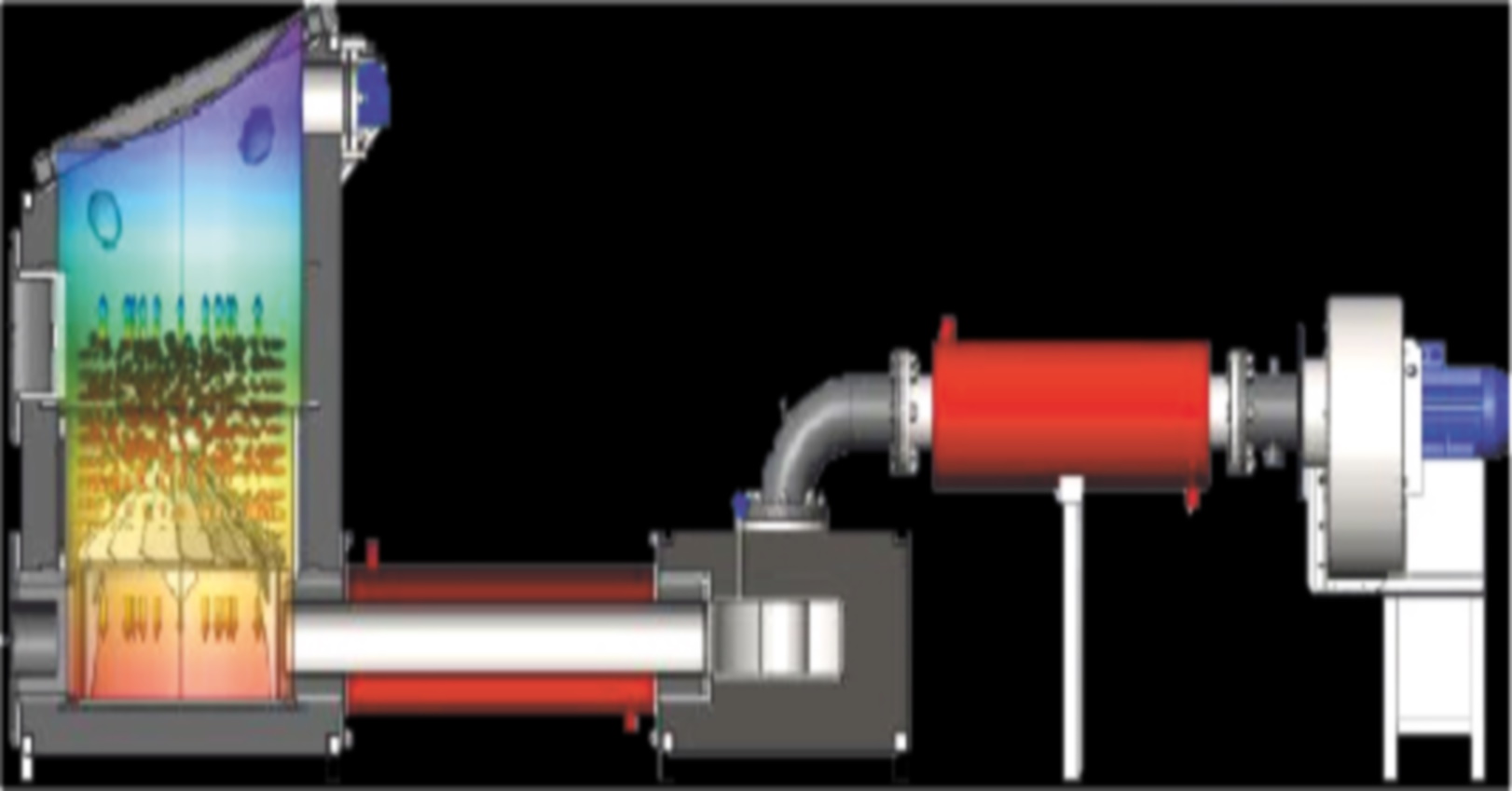
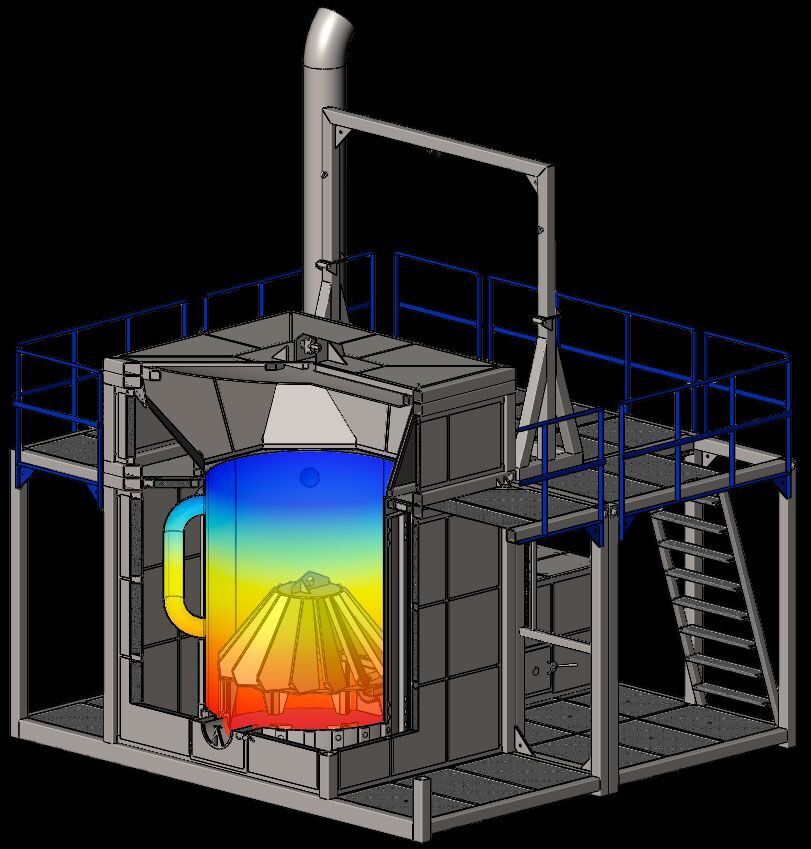
The principle of operation of the plant is based on filter combustion in the superadiabatic regime, which is achieved by the formation of a countercurrent "combustible oxidizer", the use of the generated static electric discharges (effect of the "cold" plasma at the temperature above 2000С), as well as the decomposition of the moisture contained in municipal waste into hydrogen and oxygen. This plant requires for thermal neutralization, no use of natural gas, diesel fuel or other energy sources. At the same time, the energy costs for the operation of the plant are ten times lower than the energy produced. This system consumes, for example, only 0.5-1.0 kWh of electricity, when connected to heat consumers it generates heat energy, with additional equipment with a steam-gas generator it generates electricity.
The advantage of this plant is that no prior treatment (crushing, drying, sorting) of municipal waste is required, and the amount of ash residues is 1-3% of the weight of recycled municipal organic waste.
In addition, the ash residue belongs to hazard class 5 and can be used as a filling in road construction or buried without environmental requirements. Without additional treatment, pollutant emissions into the atmosphere are within ecological limits. Compared to existing technologies for the thermal neutralization of municipal waste, including pyrolysis plants, which require additional energy resources for the conversion of municipal waste into gaseous, solid and liquid fractions, which then still need to be processed and transported to the consumer, "cold plasma" has a number of obvious advantages. However, the use of pyrolysis products is associated with significant environmental problems, and in the preparation of the pyrolysis process, the solid municipal waste must be dried and crushed beforehand.
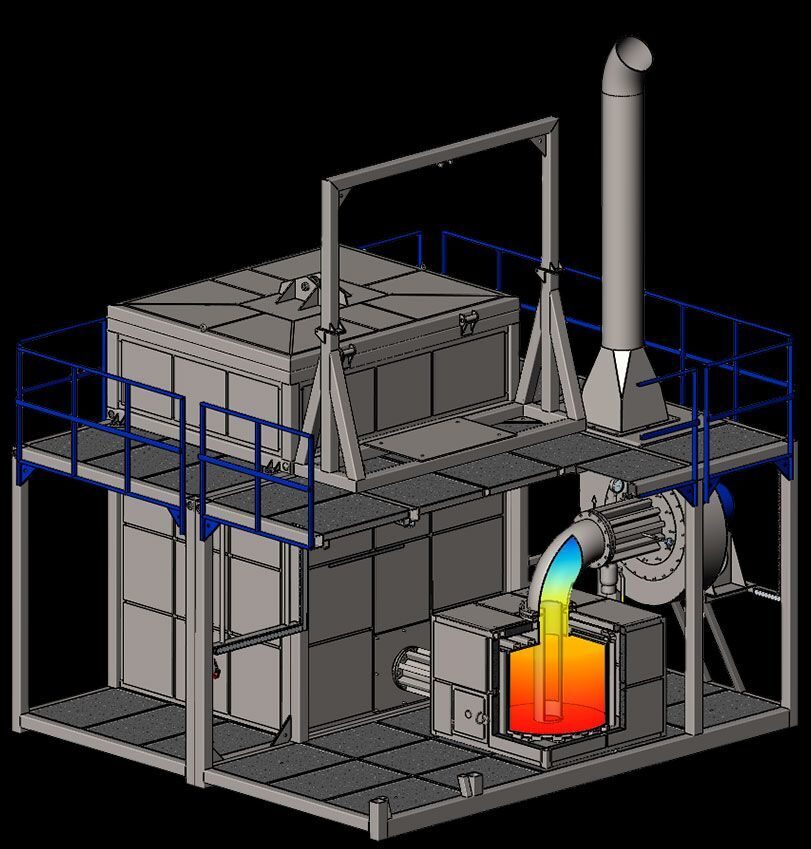
The plant is available in a modular design with a capacity of 5 to 60 m3 of solid waste per day. The plant is assembled in standard 20-foot mobile containers that can be transported by any means of transport and designed as an extension of the number of modules to the required productivity.
The basic principle of the technology is based on the destruction of the charged raw material by spontaneously occurring electrical discharges in the reactor chamber, which create a flame cloud with a temperature in the destruction zone of over 2000C. Micro-explosions occur, which cause immediate decomposition of the raw materials, releasing free carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The commercial product here is the thermal energy and inorganic residues (in the treatment of sewage sludge, up to 30% of sand is allowed.
 |
 |
 |
||||
The cold plasma reactor uses a two-chamber furnace. Superadiabatic combustion and filtration combustion are used to ensure up to 99% recovery of organic raw materials. Solid municipal waste with a moisture content of up to 80% is accepted for disposal. The main feature of combustion is the filtration of the gas, which not only participates in the chemical reaction, but also acts as a coolant, forming a thermal structure with combustion waves of two temperatures.
The plasma is characterized by high efficiency, safety and the absence of secondary contamination. Plasma recycling plants offer the advantages of high operating efficiency, low processing costs, investment savings and easy operation. The basic principle is to break down waste molecules into elementary components, and then combine these elements into harmless compounds.